Contents (go to): Introduction ¦ Background ¦ Action ¦ Theories ¦ Process

Introduction
The project will cover:
- History and background of Far-Right movements.
- Specific country examples.
Background
History of Far-Right Movements
- Can be traced back to late-19th century in Europe.
- Rise of Fascism in the 1920s and 1930s with the rise of Mussolini and Hitler.
- World War II period and increase of xenophobia and anti-Semitism.
- Post- WWII.
- Increased acknowledgement of the dangers of nationalism, white-supremacy, and fascism.

Note: The poster shows Adolf Hitler greeting Munich Nuncio Archbishop Alberto Vassallo di Torregrossa. The photograph was taken at the ground-stone laying ceremony at the “German Art Exhibition Hall” in Munich on 15 October 1933. The Vatican subsequently protested the Nazi Party’s use of the photograph for election propaganda (ushmm.org).
Application to today

- Threats of terrorism.
- Spread of far-right ideologies via social media.
- Examples of far-right groups today.
- In the US.
- In Europe.
- In Latin America and Asia
Action
Artefacts and Materials
- Hanging informational flyers around campus.
- Including a QR code for when the webpage is finished so people can access the site for more information.
- Incorporating published research and case-studies on combatting Far-Right extremism.
- On the webpage we are including links to both national and international examples on how to actively combat the spread of extremist ideologies.
Flyer 1
Counter Extremism
Includes a brief explanation of methods to counter extremism.

Flyer 2
Counter Extremism: The power of education combatting the spread of the far-right.
More detailed flyer with more information on the history of Far-Right, how current movements function, examples of threats to democracy, and what to do to combat the spread of far-right movements and ideologies.

International examples

- United States
- QAnon, increase in nationalist sentiments and xenophobia.
January 6th, 2021 an attack on the Capitol in Washington DC. - New Zealand
- Deadly terrorist attack of a mosque in Christchurch perpetrated by a far-right extremist.
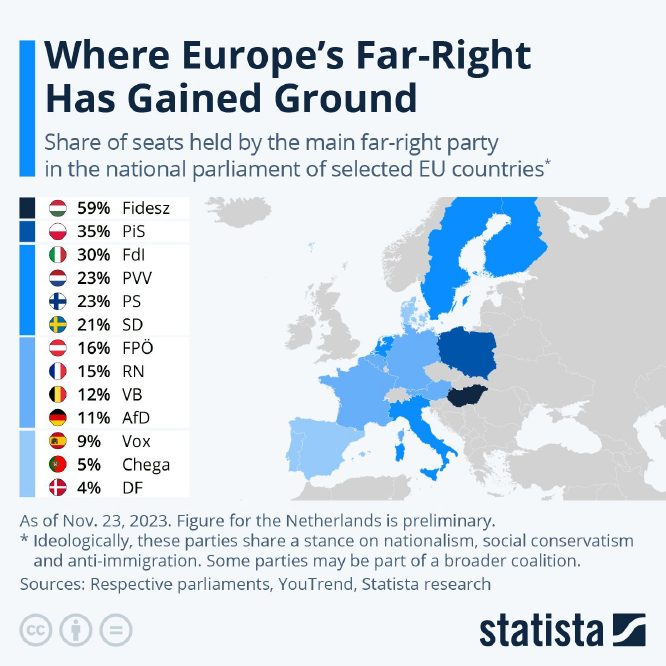
- Europe
- Syrian refugee crisis that led to an increase of nationalist and far-right sentiment in the countries where the bulk of refugees were entering.
Will there be a far-right rise here in Ireland in the coming years?
Protests against Far-Right movements

Countering Extremism
Tactics to combat the spread of Far-Right groups and disinformation
- 1. Promote inclusivity and diversity
- Strengthening the power of diversity and value of different perspectives in society.
- 2. Educate and empower youth
- Creating programs to educate youth on the dangers of far-right rhetoric.
- 3. Promote democratic values
- Emphasizing the importance of rule of law and democratic institutions.
- 4. Support community engagement
- Creating a sense of community brings us together.
- 5. Combat hate speech and disinformation
- Encouraging social media literacy, critical thinking, and fact-checking.
Theoretical Framework
Some key theoretical frameworks we used to help understand our project material and develop our analysis.
Political & Historical Lens
- Nationalism.
- Populism.
- Ethnic & Racial Identity.
Sociological Lens
- Frame Analysis.
- Social Identity Theory.
- Cultural Theory.
Process
- Brainstorming.
- Discussion.
- Group meetings.
- Delegation of tasks based on skills and interests.
- Sharing research and summaries on shared documents.
- Creating action plan.
- Developing flyers with pertinent information.
- Reading PowerPoint.
- Reviewing information for class presentations.
- Presenting.
- Sharing flyers around campus.
Conclusion
In this collaboration, the team worked well together with high efficiency during discussions and mutual cooperation. I also experienced strong leadership skills from leaders and organizers in the group, which is something I need to learn.
Regarding my contributions to background research and theoretical frameworks, I mainly utilized PowerPoint presentations during seminars to seek feedback and improvements from group members. Additionally, I extensively researched various sources, compared Chinese and Western materials, contrasted extreme left and extreme right ideologies to gain a clearer understanding of the development and dangers of extremist ideologies.
Conducting interviews with education majors, I gathered insights on how to prevent the spread of extremist forces in the online domain and mitigate their harms in real world teaching scenarios. Finally, I summarized my findings. Throughout this process, I deeply realized the real-world dangers of extremist ideologies and how they impact societal change. It’s imperative to learn from historical experiences in combating extremist ideologies. Lastly, I express my gratitude to the professor for their dedicated teaching. This semester’s study abroad experience has been enriching, and I am sincerely thankful.
Authors
Foley Cian, Wenyu & Yaodi.